常见的排序算法
萌新接触排序算法—JS & Java实现
写在前面: 下面的排序都对整形类型的数组进行排序,并且为升序(ascending)排序
选择排序
先确定一个位置上的数,接着处理后续位置的元素。即在n个元素的数组中,找出n个元素的最大值或最小是,排到第1个元素位置上,然后屏蔽第1个元素,从第2个元素起,找出剩下n-1个元素的最大值,排在第2个元素的位置上面…以此类推
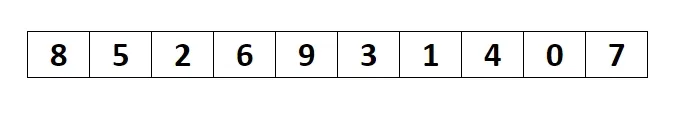
function selectionSort(nums) {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
let currentMin = nums[i];
let currentMinIndex = i;
for (let j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] < currentMin) {
currentMin = nums[j];
currentMinIndex = j;
}
}
if (currentMinIndex !== i) {
// swap
nums[currentMinIndex] = nums[i];
nums[i] = currentMin;
}
}
}插入排序
数组分为了排序好了的部分(前)和未排序的部分(后),从未排序部分中取出一个元素,逐一与排序好了的部分的元素进行比较,以插入该部分中去。
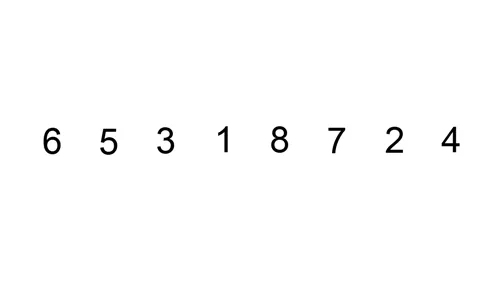
function insertionSort(nums) {
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
let k = i - 1;
let current = nums[i];
while (k >= 0 && nums[k] > current) {
nums[k + 1] = nums[k];
k--;
}
nums[k + 1] = current;
}
}希尔排序
(待更)
冒泡排序
可以把数组想象为横着的水池,数组的相邻元素进行两两比较,里面较大或较小的元素就会慢慢地“浮”到最右边或最左边
不过,我们可以考虑一下,不与排好了的部分进行比较
function bubbleSort(nums) {
for (let k = 1; k < nums.length; k++) {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length - k; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i +1]) {
const tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[i + 1];
nums[i + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}并且还加入一个boolean进行判断整个数组是否已经排序完毕
function bubbleSort(nums) {
let needNextPass = true;
for (let k = 1; k < nums.length && needNextPass; k++) {
needNextPass = false;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length - k; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i +1]) {
const tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[i + 1];
nums[i + 1] = tmp;
needNextPass = true;
}
}
}
}归并排序
这个排序涉及到分治(Divide-and-Conquer即分而治之)的方法。将数组进行分割然后进行排序,之后将排序的结果一个一个地合并起来
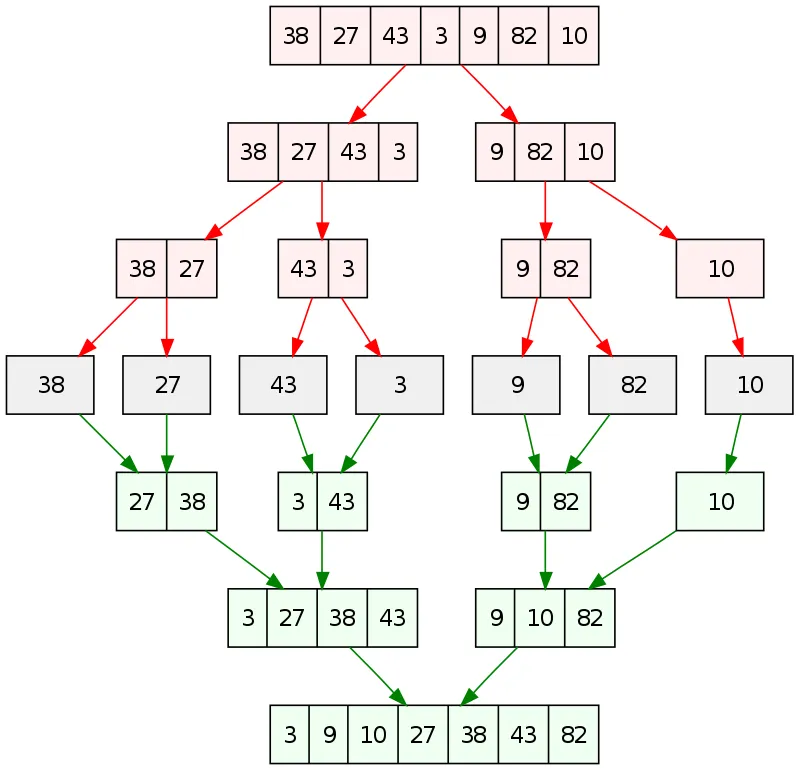
代码实现如下,使用递归,将数组分开与合并
function mergeSort(nums) {
if (nums.length > 1) {
const firstHalf = nums.slice(0, nums.length / 2);
mergeSort(firstHalf);
const secondHalf = nums.slice(nums.length / 2);
mergeSort(secondHalf);
merge(firstHalf, secondHalf, nums);
}
}
// merge two sorted arrays
function merge(nums1, nums2, tmp) {
let current1 = 0;
let current2 = 0;
let current3 = 0;
while (current1 < nums1.length && current2 < nums2.length) {
if (nums1[current1] < nums2[current2]) {
tmp[current3++] = nums1[current1++];
} else {
tmp[current3++] = nums2[current2++];
}
}
while (current1 < nums1.length) {
tmp[current3++] = nums1[current1++];
}
while (current2 < nums2.length) {
tmp[current3++] = nums2[current2++];
}
}快速排序
跟归并排序相似但不完全一样。大致思路如下
- 选取数组的一个主元pivot
- 对该数组进行排序---小于或等于该主元的元素成为子数组1(不包括主元),大于主元元素的元素成为子数组2
- 如果这些个数组的长度依旧大于1,继续对该两个数组进行该操作
伪代码如下
suppose there is an array named list
function quickSort(list) {
if (list.length > 1) {
select a pivot;
partition the list into list1 and list2 that satisfy
1. all elements in list1 are <= pivot;
2. all elements in list2 are > pivot;
quickSort(list1);
quickSort(list2);
}
}JS实现如下
function quickSort(nums, first, last) {
if (!first && !last) {
quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
} else if (first < last) {
const pivotIndex = partition(nums, first, last);
quickSort(nums, first, pivotIndex - 1);
quickSort(nums, pivotIndex + 1, last);
}
}
function partition(nums, first, last) {
const pivot = nums[first];
let low = first + 1;
let high = last;
while (high > low) {
// search
while (low <= high && nums[low] <= pivot) {
low++;
}
while (low <= high && nums[high] > pivot) {
high--;
}
// swap
if (high > low) {
const tmp = nums[low];
nums[low] = nums[high];
nums[high] = tmp;
}
}
// swap pivot with list[high]
if (pivot > nums[high]) {
nums[first] = nums[high];
nums[high] = pivot;
return high;
} else {
return first;
}
}堆排序
该排序算法使用完全二叉树来进行排序
完全二叉树指的就是,一棵深度为k的树,其他深度的节点的度都要为2(即其余层为满的),除了深度为k(最后一层)的节点可以为满,也可以是右边缺少若干节点。
如果一棵完全二叉树树为堆的话,那么就会有这个性质---每个节点的大小比它的每一个child都要大
下图(By Kelott - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=99968794)
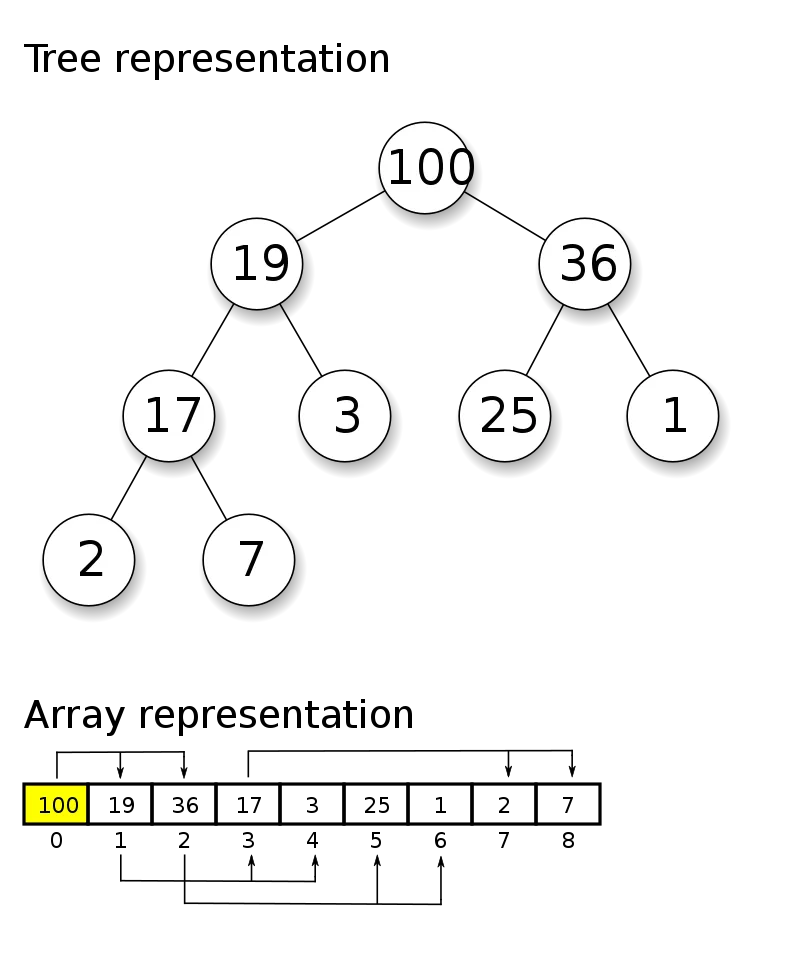
上面的这个图片表示的就是一个Heap,还有有父子节点在数组上的关系
leftChildIndex = 2 * fatherIndex + 1
rightChildIndex = 2 * fatherIndex + 2往堆上添加元素的时候,元素会添加到数组最后一个位置上,然后与父节点作比较,大于或小于的话就交换位置,直到父节点小于或大于这个元素
去除元素的时候,是把根节点元素取出,然后把最后一个元素放置于根节点上,接着让这个元素与子节点进行比较与交换,使得最后结果还是一个堆。
Heap的实现如下
class Heap {
constructor(objects) {
this.list = [];
if (Array.isArray(objects)) {
objects.forEach(o => this.add(o));
}
}
add(newObj) {
this.list.push(newObj);
let currentIndex = this.list.length - 1;
while (currentIndex > 0) {
let parentIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2;
if (this.list[currentIndex] > this.list[parentIndex]) {
const tmp = this.list[currentIndex];
this.list[currentIndex] = this.list[parentIndex];
this.list[parentIndex] = tmp;
} else {
break;
}
currentIndex = parentIndex;
}
}
remove() {
if (this.list.length === 0) return null;
const removedObject = this.list[0];
this.list[0] = this.list[this.list.length - 1];
this.list.pop();
let currentIndex = 0;
while (currentIndex < this.list.length) {
const leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
const rightChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 2;
if (leftChildIndex >= this.list.length) break;
let maxIndex = leftChildIndex;
if (this.list[leftChildIndex] < this.list[rightChildIndex]) {
maxIndex = rightChildIndex;
}
if (this.list[currentIndex] < this.list[maxIndex]) {
const tmp = this.list[maxIndex];
this.list[maxIndex] = this.list[currentIndex];
this.list[currentIndex] = tmp;
currentIndex = maxIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
return removedObject;
}
}(待更)
桶排序
把数据都分开到几个桶里头
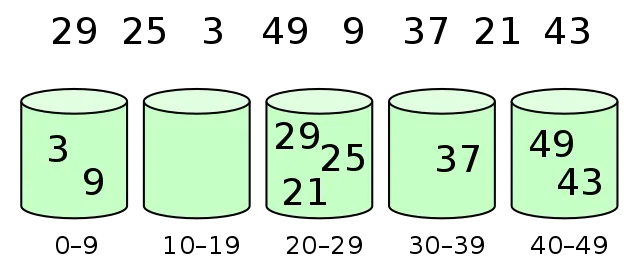
分别对这几个桶进行排序,接着把排序好的结果归到一起。完成排序。
当均匀分布时,最为高效。(时间复杂度慢慢加
function bucketSort(nums, bucketSize) {
// find max and min
let max = Number.MIN_VALUE;
let min = Number.MAX_VALUE;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < min) { min = nums[i]; }
if (nums[i] > max) { max = nums[i]; }
}
// generate buckets
const DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;
bucketSize = bucketSize || DEFAULT_SIZE;
const bucketCount = Math.floor((max - min) / bucketSize + 1);
const buckets = Array(bucketCount);
for (let i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) {
buckets[i] = Array();
}
// push nums into bucket
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
const index = Math.floor((nums[i] - min) / bucketSize);
buckets[index].push(nums[i]);
}
// sorted on each bucket
console.log(buckets)
buckets.forEach(bucket => insertionSort(bucket));
// push result into an array
let sorted = [];
buckets.forEach(bucket => bucket.forEach(e => sorted.push(e)));
return sorted;
}
function insertionSort(nums) {
for (let k = 1; k < nums.length; k++) {
let current = nums[k];
let i = k - 1;
while (i >= 0 && nums[i] > current) {
nums[i + 1] = nums[i];
i--;
}
nums[i + 1] = current;
}
}基数排序
但是桶排序不是稳定的,会受到桶的分配情况、元素个数、桶的个数的影响。
如果我们只需要进行数字的排序的话,我们就可以用基数排序。这个是稳定的算法,在时间上,复杂度为O(dn),d为位数

自己写的伪代码…
let n=1, nums=an array of numbers
while (n <= the digit of the maximum number in the list) {
1. push the number to the n th bucket ,according to the number's n th digit from right to left.
(For example, when n=2, 697->9 and 9(009)->0)
2. gather the elements from bucket[0] to [9] one by one
3. clear nums and let nums = these gathered elements
n++
}JS实现如下
function radixSort(nums) {
const buckets = Array(10);
const max = Math.max(...nums);
const digit = Math.ceil(Math.log10(max));
for (let currentDiv = 1; currentDiv <= Math.pow(10, digit) ; currentDiv *= 10) {
// clear the arrays
for (let i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = Array();
}
let newNums = [];
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] / currentDiv >= 1) {
buckets[Math.floor(nums[i] / currentDiv) % 10].push(nums[i]);
} else {
buckets[0].push(nums[i]);
}
}
buckets.forEach(b => b.forEach(e => newNums.push(e)));
nums = newNums;
}
return nums;
}外部排序
其实思路跟归并排序,是差不多的。只不过这里的条件有点不同—即我们需要排序一个大文件里头的数字,由于规模非常大,我们不可能一次性把它们全部加载进内存里头。
因此,我们可以把这个文件其中分为定长(segmentSize)的许多片段(Segment),每一个片段进行排序。(下面是依次把每一个排序好的子数组放入一个文件里头)
之后,再将这些个片段,两两归并到一起排序。排序之后,将片段数减半,片段长度加倍,(递归)反复这样排序,操作下去,直到最后,就会得到一个排序好了的文件。
代码实现(Java)如下,先随机创建一个含有很多数字的文件,然后对该文件进行外部排序。
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ExternalSort {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
createFile();
sort("largedata.dat", "sortedfile.dat");
try (DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("sortedfile.dat"))) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.print(input.readInt() + " ");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void createFile() {
try (
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("largedata.dat")))
) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5000000; i++) {
output.writeInt((int)(Math.random() * 100000));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static int initializeSegments(int segmentSize, String originalFile, String f1) throws Exception {
int[] list = new int[segmentSize];
DataInputStream input = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(originalFile))
);
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f1))
);
int numberOfSegment = 0;
while (input.available() > 0) {
int i = 0;
for ( ; input.available() > 0 && i < segmentSize; i++) {
list[i] = input.readInt();
}
Arrays.sort(list);
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
output.writeInt(list[j]);
}
}
input.close();
output.close();
return numberOfSegment;
}
private static void copyHalfToF2(int numberOfSegments,
int segmentSize, DataInputStream f1, DataOutputStream f2) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < segmentSize / 2 * numberOfSegments; i++) {
f2.writeInt(f1.readInt());
}
}
private static void mergeSegments(int numberOfSegments,
int segmentSize,
DataInputStream f1, DataInputStream f2, DataOutputStream f3) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfSegments; i++) {
mergeTwoSegments(segmentSize, f1, f2, f3);
}
while (f1.available() > 0) {
f3.writeInt(f1.readInt());
}
}
private static void mergeTwoSegments(int segmentSize, DataInputStream f1, DataInputStream f2,
DataOutputStream f3) throws Exception {
int intFromF1 = f1.readInt();
int intFromF2 = f2.readInt();
int f1Count = 1;
int f2Count = 1;
while (true) {
if (intFromF1 < intFromF2) {
f3.writeInt(intFromF1);
if (f1.available() > 0 || f1Count++ >= segmentSize) {
f3.writeInt(intFromF2);
break;
} else {
intFromF1 = f1.readInt();
}
} else { // intFromF1 >= intFromF2
f3.writeInt(intFromF2);
if (f2.available() > 0 || f2Count++ >= segmentSize) {
f3.writeInt(intFromF1);
break;
} else {
intFromF2 = f2.readInt();
}
}
}
while (f1.available() > 0 && f1Count++ < segmentSize) {
f3.writeInt(f1.readInt());
}
while (f2.available() > 0 && f2Count++ < segmentSize) {
f3.writeInt(f2.readInt());
}
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = 100000;
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 100000;
private static void sort(String sourceFile, String targetFile) throws Exception {
// phase 1
int numberOfSegments = initializeSegments(MAX_ARRAY_SIZE, sourceFile, "f1.dat");
// phase 2
merge(numberOfSegments, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE, "f1.dat", "f2.dat", "f3.dat", targetFile);
}
private static void merge(int numberOfSegments, int segmentSize,
String f1, String f2, String f3, String targetFile) throws Exception {
if (numberOfSegments > 1) {
mergeOneStep(numberOfSegments, segmentSize, f1, f2, f3);
merge((numberOfSegments + 1) / 2, segmentSize * 2,
f3, f1, f2, targetFile);
} else {
File sortedFile = new File(targetFile);
if (sortedFile.exists()) sortedFile.delete();
new File(f1).renameTo(sortedFile);
}
}
private static void mergeOneStep(int numberOfSegments, int segmentSize,
String f1, String f2, String f3) throws Exception {
DataInputStream f1Input = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f1), BUFFER_SIZE)
);
DataOutputStream f2Output = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f2), BUFFER_SIZE)
);
copyHalfToF2(numberOfSegments, segmentSize, f1Input, f2Output);
f2Output.close();
DataInputStream f2Input = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f2), BUFFER_SIZE)
);
DataOutputStream f3Output = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f3), BUFFER_SIZE)
);
mergeSegments(segmentSize / 2, segmentSize, f1Input, f2Input, f3Output);
f1Input.close();
f2Input.close();
f3Output.close();
}
}